Not being a separate independent disease, but only a complication against the background of existing disorders, pathological glial changes in the brain occur both in adults and in newborn babies.
They are characterized by damage to the cells of the central nervous system and structural changes in tissues, partial or complete dysfunction of neural connections. And, if in old age the concept of brain gliosis means aging of the organ, then in children and adolescents it is a consequence, mainly, of another chronic or well-formed disease.
It is not possible to detect a neurological disorder on your own. Only thanks to a modern non-invasive procedure, such as magnetic resonance imaging, a specialist is able to evaluate the neuromuscular apparatus and brain structures, find pathologies of nerves and blood vessels, including gliosis of the brain and spinal cord.
Let us consider in more detail how this violation occurs.
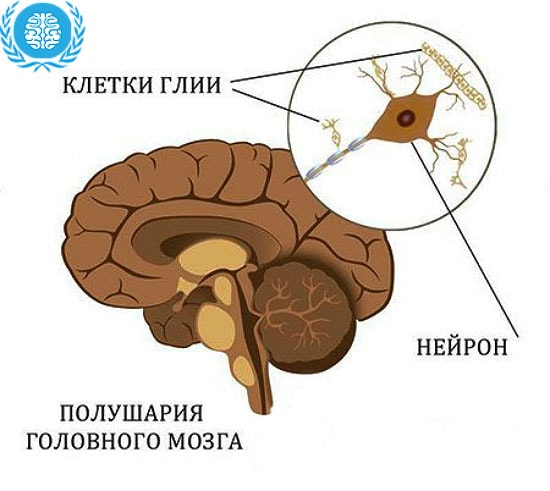
In a healthy person, neurons, glia, and nerve nodes provide a close, inextricable link between the central nervous system and all organs and tissues. And each of them carries a specific task.
Excitable neurons transmit signals to muscles and glands, glial cells are involved in metabolic processes and provide protection and the necessary conditions for the full transmission of the impulse signal. The accumulation of glial, nerve cells and their processes are collected in the nerve nodes.
Under conditions of natural functioning of the CNS, glial cells, when neurons are damaged, are able to replace them, to distinguish dead segments from healthy adjacent tissues. Thus, they prevent damage to the entire brain. But the reverse process is also possible, when glia begin to multiply, causing deformation and death of healthy nerve cells.
This is what gliosis of the brain is, the result of which is the extensive replacement of neurons with glial cells. This process is considered quite natural in old age. Other categories that are susceptible to pathology need additional study of the problem.
Causes of gliosis
Unfortunately, the growth of glial cells is observed in newborns due to a hereditary factor in 25% of cases.
The life expectancy of such children is no more than 2-4 years. Since, in most cases, it is not detected immediately. The child develops normally up to six months. After that, the deterioration of reflex functions and the diagnosed death of brain cells begin abruptly.
Another reason why gliosis develops in a child with damage to brain cells is birth trauma and oxygen starvation.
Contribute to the increase in necrotic areas and disruption of the nervous system bad habits. This is not only smoking and alcohol, but also a large consumption of fatty, cholesterol-rich foods.
The vital functions of the body under the influence of adverse conditions are threatened and lead to the inflammatory process of the hypothalamus, which loses the ability to regulate the processes and reactions that occur in the nervous and endocrine systems.
Irreversible destruction of neurons provoke craniocerebral trauma. Characterized by small foci or macrostructural damage to the substance of the brain. The consequence of damage to the brain tissues, membranes, blood vessels and nerve cells is cerebral edema and the formation of vasogenic foci with the release of plasma into the white matter.
At the age of 15-40 years, gliosis of the white matter of the spinal cord and brain is observed more often.
The appearance of foci of destruction occurs against the background of the formation of so-called plaques that affect the nerve fibers in the disease of multiple sclerosis.
Tuberculosis also leads to weakness of neurons and increased activity of glial cells, when mycobacteria infect the meninges and hemispheres, choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and cause necrosis of large areas of the nervous system.
Gliosis of the brain: affected areas
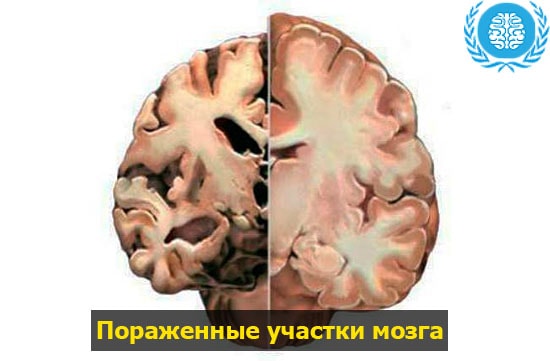
Hardware diagnostics using MRI and the experience of specialists gained in the course of long-term studies makes it possible to consider the pathology depending on where the glial foci are located in the brain.
There are several types of affected segments.
Periventricular. Often accompanied by the presence of cysts. It is located in the ventricles of the brain.
diffuse. A characteristic focus of gliosis is observed both in the white matter of the brain and in the region of the spinal cord.
Perivascular. This type is characterized by the accumulation of glial cells in the area of sclerotic lesions. Most often it is considered in the form of gliosis of vascular origin.
Anisomorphic. Glial cells are located randomly in the hemispheres of the main organ of the CNS.
Marginal. It occurs under the shells of brain regions.
isomorphic, located in a clear sequence of glial transformation.
Subepindymal. Violation of neurons occurs in a thin layer of the epithelial membrane of the ventricles or spinal cord.
The meninges are destroyed by a characteristic marginal lesion.
The predominance of glial cells over nerve cells is expressed by a fibrous type of gliosis in the brain.
Single, smallest altered segments appear naturally, as a result of abnormal labor activity or are associated with age-related changes in the body, while multiple foci of gliosis of the brain indicate the presence of a source, the cause of the pathology. Accompanied by a deterioration in the health of the patient.
Signs of gliosis

The vast majority of patients who turn to a neurologist for advice describe a condition associated with impaired functioning of the organs of the nervous system.
In order to recognize the symptoms of incipient gliosis of the brain, to explain what it is, it is enough for a specialist to get acquainted with the complaints of a person.
Frequent dizziness and migraine, paresis of the limbs and impaired coordination of movements, jumps in blood pressure and convulsions are signs of damage to the central nervous system. May be accompanied by loss of vision and hearing, distracted attention and memory problems. Sometimes there are hallucinations, consciousness is distorted.
Diagnostics
Requires special accuracy and correctly diagnosed pathology of the brain. But methods for studying destruction are not enough. Brain MRI remains the most informative and most reliable in the diagnosis of gliosis today.
With the help of this scanning procedure, it is possible to recognize changes that have undergone not only vessels and nerve cells, brain, cortex, but also the pituitary gland.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the results of a brain MRI for gliosis must confirm the presence of black and white spots in the image. They usually come from glial cells. The centers of already formed growths can be counted, to find out their size.
When performing CT, a hypodense, dark, low-density area of the cerebral cortex is visualized. Often it is subject to dystrophic changes.
Gliosis found in the white matter or peripheral parts of the brain is recommended to be treated. The prognosis for the patient is favorable. If the localization of glial cells is observed in the stem part or gray matter of the thalamus, complications are possible.
Treatment of gliosis of the brain

The lack of information and the pathology not fully understood complicates the search for effective means leading to recovery. To cope with severe disorders of the nervous system, which were caused by structural changes in the brain, drugs help at the initial stage.
To restore an exhausted body, ascorbic acid, vitamins B, P, E are prescribed.
To increase the stability of the brain, activate the functions of the central nervous system, it is mandatory to take nootropic drugs, such as Glycised and Piracetam.
With headache attacks, analgesics help: "Ketanov", "Analgin".
They also prescribe drugs that improve metabolism and restore the activity of the nervous system: Actovegin and Cinnarizin.
Statins and fibrates prevent platelet aggregation, lower cholesterol levels, have an anti-inflammatory effect and restore blood vessels. Fenofibrate, Simvastatin, Livostor.
The treatment of gliosis of the brain does not end there. It is important to follow a special diet, which provides for the rejection of fatty foods. The diet should consist mainly of fruits, vegetables, grains and plenty of fluids.
The use of alcoholic beverages, narcotic and psychotropic drugs is prohibited. You will also have to quit smoking. In order to prevent gliosis, proper rest, sports and fresh air, the absence of stress and mental work during the rehabilitation period are necessary.



