According to medical statistics, spontaneous miscarriage occurs in 15-20% of the fairer sex. Under this term, doctors mean independent, independent of the will of the woman, pathological for a period not exceeding 20 weeks. Otherwise, miscarriages are called spontaneous abortions. It should be distinguished from artificial abortion, carried out in a hospital at the request of a woman or the testimony of doctors.
Classification and causes of spontaneous abortions
A miscarriage that occurs in a pregnant woman for a period not exceeding 12 weeks is considered early. If a spontaneous abortion occurred between 13 and 20 weeks, then it is called late. Most often, spontaneous abortion occurs in the early stages, so it can be argued that the risk of fetal loss is higher in the first trimester of pregnancy.
What reasons can be the culprits of a miscarriage? To date, doctors call many factors that affect spontaneous termination of pregnancy. These include:
- genetic abnormalities in the development of the embryo, due to which it is not adapted to life;
- sexual diseases (trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis);
- TORCH infections (toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes);
- hormonal abnormalities in a woman's body (thyroid disease, diabetes, progesterone deficiency, an excess of male hormones, etc.);
- incompatibility of Rh factors in a pregnant woman and her fetus;
- anomalies in the anatomical structure of the uterus (saddle-shaped, unicornuate, bicornuate, with an internal septum), intrauterine fusion (synechia), submucosal uterine myoma;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency, as a result of which the isthmus and cervix do not withstand the pressure of a growing embryo and spontaneously open;
- taking certain groups of medications (for example, analgesics or hormonal contraceptives);
- stressful situations;
- bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs);
- ARI, SARS;
- shaking in transport;
- excessive physical activity;
- taking hot baths;
- active sex life;
- the presence of miscarriages or induced abortions in the past.
Symptoms of miscarriages
 Women who have recently become pregnant or are planning to do so in the near future need to familiarize themselves with how a miscarriage occurs. This knowledge will help them avoid unwanted termination of pregnancy. Spontaneous abortion begins with unpleasant pulling pains in the lower abdomen, very similar to those that any woman faces on the first day of menstruation. Painful sensations indicate the beginning of the contractile activity of the uterus, that is, a condition in which there is a threat of spontaneous abortion.
Women who have recently become pregnant or are planning to do so in the near future need to familiarize themselves with how a miscarriage occurs. This knowledge will help them avoid unwanted termination of pregnancy. Spontaneous abortion begins with unpleasant pulling pains in the lower abdomen, very similar to those that any woman faces on the first day of menstruation. Painful sensations indicate the beginning of the contractile activity of the uterus, that is, a condition in which there is a threat of spontaneous abortion.
In the case when a woman does not have time to see a doctor in time, the pathological process will continue to progress. Drawing pains of moderate intensity are replaced by strong and cramping. They cover not only the lower abdomen, but also the groin, the lumbar region. In parallel with this, spotting spotting appears from the genitals of the pregnant woman. This condition is called in the medical literature "beginning miscarriage." It is characterized by gradual detachment of the placenta. With the onset of a miscarriage, the fetal egg still continues to be in the uterine cavity, however, its canal begins to open, which at any time can result in an independent termination of pregnancy.
When the fetal egg detaches from the uterine wall, a woman is diagnosed with an incomplete or complete miscarriage. If this happens, no measures will be able to save the child in the womb. A complete miscarriage is a condition in which the entire embryo exits the uterine cavity. This process is accompanied by severe bleeding from the genitals. There are large clots in the secretions. As the uterus contracts, blood loss becomes less, and then completely stops.
 Incomplete miscarriage is an independent termination of pregnancy, in which the fetal egg does not completely leave the uterine cavity. At the same time, part of it will continue to remain inside, provoking severe bleeding in a woman. They will continue until the complete release of the remnants of the egg or until the gynecological cleaning (curettage) of the uterine cavity.
Incomplete miscarriage is an independent termination of pregnancy, in which the fetal egg does not completely leave the uterine cavity. At the same time, part of it will continue to remain inside, provoking severe bleeding in a woman. They will continue until the complete release of the remnants of the egg or until the gynecological cleaning (curettage) of the uterine cavity.
Knowing what the symptoms of a miscarriage are, a woman in the first months of pregnancy should monitor her well-being. If pain occurs in the lower abdomen or other signs of spontaneous abortion described above, she should immediately contact a gynecologist. The sooner she does this, the more chances she will have to keep the pregnancy.
Diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous abortions
To determine the threat of miscarriage in a patient for a doctor today is not a problem. When examining a pregnant woman in a gynecological chair, the doctor pays attention to the uterus. An increased tone of the uterus, a discrepancy between its size and the gestational age and insufficient closure of its cervix indicate a condition that threatens the expectant mother. Also, the gynecologist conducts an external examination of the discharge from the female genital organs. In the normal course of pregnancy, they should be transparent, mucous, without blood impurities.
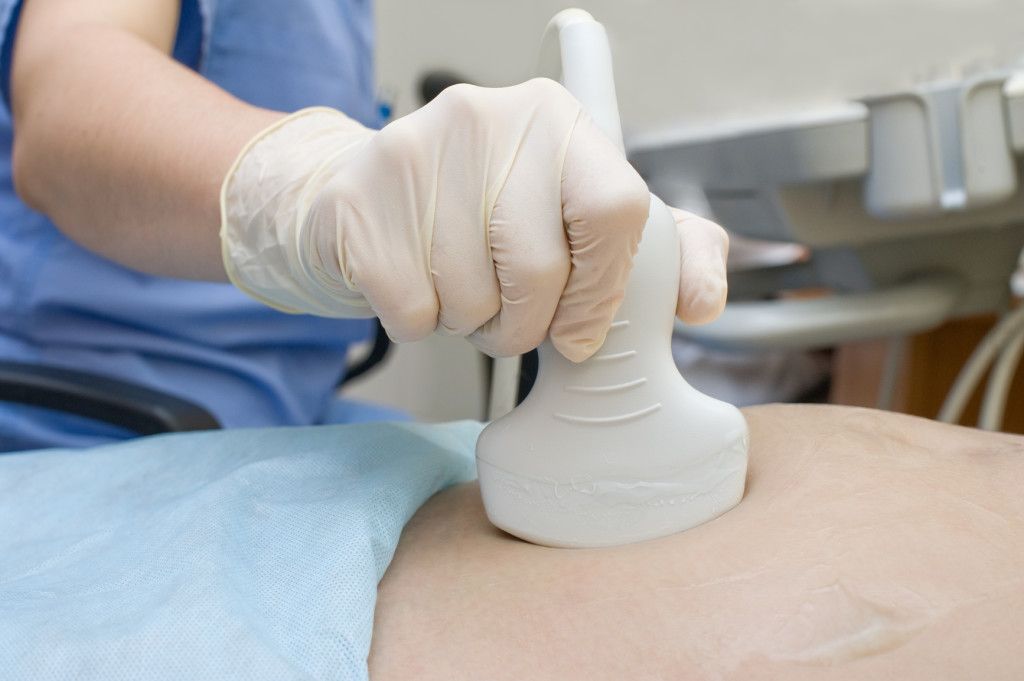 If a threat of miscarriage is suspected, the gynecologist directs the patient to an ultrasound scan, which is used to examine the uterus and its contents. Ultrasound allows you to determine such signs of a threatened abortion, such as placental abruption, uterine tone, and low fetal position. In the case when a woman is diagnosed with a "threat of spontaneous abortion", she is necessarily sent for treatment in a hospital.
If a threat of miscarriage is suspected, the gynecologist directs the patient to an ultrasound scan, which is used to examine the uterus and its contents. Ultrasound allows you to determine such signs of a threatened abortion, such as placental abruption, uterine tone, and low fetal position. In the case when a woman is diagnosed with a "threat of spontaneous abortion", she is necessarily sent for treatment in a hospital.
If the patient is diagnosed with a threatened miscarriage, after hospitalization she will be prescribed treatment, the purpose of which will be to maintain the existing pregnancy. With the onset of spontaneous abortion with a slight detachment of the placenta and moderate blood discharge, the expectant mother will also be shown therapy aimed at preventing further progression of the pathology and preserving the fetus. The drugs used in these cases include:
- antispasmodics that help relieve uterine tone;
- gestagens that correct the level of the main pregnancy hormone - progesterone;
- glucocorticoids that normalize the hormonal background in hyperandrogenism;
- sedatives of plant origin;
- vitamins B9, E, Magne B6.
 In the case when a miscarriage was avoided, the pregnant woman after discharge from the hospital will need to take the drugs prescribed by the doctor for some time. So that the threat of miscarriage does not happen again, the expectant mother is recommended a calm lifestyle and abstinence from sexual intercourse. To prevent spontaneous abortion, a woman needs to include foods rich in complex carbohydrates, fiber and calcium in her diet. These include pasta, wholemeal bakery products, vegetables, fruits, berries, cottage cheese, hard cheese and sour milk drinks.
In the case when a miscarriage was avoided, the pregnant woman after discharge from the hospital will need to take the drugs prescribed by the doctor for some time. So that the threat of miscarriage does not happen again, the expectant mother is recommended a calm lifestyle and abstinence from sexual intercourse. To prevent spontaneous abortion, a woman needs to include foods rich in complex carbohydrates, fiber and calcium in her diet. These include pasta, wholemeal bakery products, vegetables, fruits, berries, cottage cheese, hard cheese and sour milk drinks.
With heavy bleeding and placental abruption, it no longer makes sense to save the pregnancy. Treatment here consists in scraping out of the uterine cavity the remaining parts of the fetus inside it. With a late spontaneous abortion, a woman is shown a medical method of treatment.
To accelerate the contractile function of the uterus, the patient is injected with Oxytocin intravenously, and antibacterial drugs are prescribed to prevent the development of the inflammatory process after cleaning. Additionally, to improve uterine contraction, women after a miscarriage are recommended to apply a heating pad filled with cold water to the lower part of the peritoneum for a short time.
 If the culprit of the spontaneous abortion was a negative Rh blood factor in a woman, then to prevent a second miscarriage, she is injected intramuscularly or intravenously with anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin. The drug is used after cleaning.
If the culprit of the spontaneous abortion was a negative Rh blood factor in a woman, then to prevent a second miscarriage, she is injected intramuscularly or intravenously with anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin. The drug is used after cleaning.
A woman who plans to become pregnant again in the future, after discharge from the hospital, will need to undergo an examination of the body to find out the cause of the spontaneous abortion that has occurred and prevent its recurrence in the future.
To do this, you will need to pass a hemostasiogram, a coagulogram, tests for a number of hormones, various urogenital and TORCH infections. In addition, the woman will be advised to undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, and the remains of the fetus will be subject to cytogenetic examination.
Miscarriages: a description of the appearance and complications after them
Often, expectant mothers ask themselves: what does a miscarriage look like? Its appearance depends on the period in which it occurred. In the first few weeks of pregnancy, it is spotting, reminiscent of those that women experience during menstruation. Late spontaneous abortion looks like a large bloody clot or bubble, inside which you can easily see the blood vessels.
Having noticed signs of a miscarriage, a woman is obliged to seek medical help, otherwise a spontaneous abortion can end in serious consequences for her.
The most common complications after miscarriages include hemorrhagic shock after severe blood loss, sepsis, infectious diseases, and the inability to bear a child in the future.



